How Does Architecture Incorporate Principles Of Earthquake-resistant Design In Structures?
 Earthquakes are some of the most unpredictable natural disasters that can cause immense damage to buildings and infrastructure. When an earthquake hits, it can cause a lot of destruction, and it is crucial to have structures that can withstand the force of the earthquake. Earthquake-resistant structures are designed to withstand the forces of an earthquake and minimize damage. In this post, we will be discussing earthquake-resistant structures and how they can help save lives and property while ensuring safety and security.
Earthquakes are some of the most unpredictable natural disasters that can cause immense damage to buildings and infrastructure. When an earthquake hits, it can cause a lot of destruction, and it is crucial to have structures that can withstand the force of the earthquake. Earthquake-resistant structures are designed to withstand the forces of an earthquake and minimize damage. In this post, we will be discussing earthquake-resistant structures and how they can help save lives and property while ensuring safety and security.
What are earthquake-resistant structures?
Earthquake-resistant structures are buildings that are designed to withstand the shaking and cracking caused by seismic waves. These buildings are constructed with materials and methods that can absorb the energy of an earthquake and minimize damage to the structure.
Why are earthquake-resistant structures important?
Earthquake-resistant structures are essential because they can save lives and minimize property damage caused by an earthquake. Buildings designed to withstand the forces of an earthquake are typically stronger and more durable than regular buildings. By ensuring that buildings and other structures are earthquake-resistant, we reduce the risk of buildings collapsing or suffering extensive damage, which can result in loss of life and a significant economic impact.
How are earthquake-resistant structures built?
Several techniques and materials are used to make earthquake-resistant structures. Here are some of the key features:
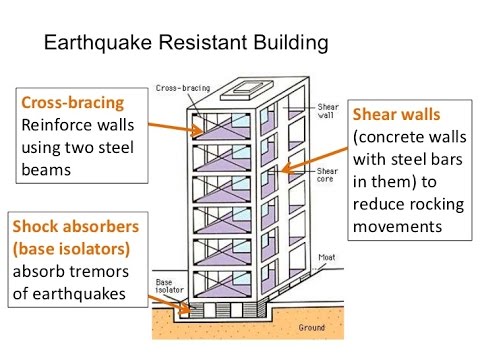
- Base isolation: This involves installing a structure on a series of bearings that can absorb the energy of an earthquake. These bearings are designed to move with the earthquake, reducing the impact on the building.
- Flexible frames: These buildings are designed to be more flexible, allowing them to bend and sway during an earthquake. Rather than resisting the forces of an earthquake, the building can absorb and dissipate the energy.
- Reinforced concrete: Reinforcing steel and concrete structures can make them more resistant to earthquake forces. Buildings constructed with reinforced concrete can withstand more ground motion than those built with conventional materials.
- Shear walls: Shear walls are vertical elements in a building that can resist lateral forces and protect the building from collapsing. These walls are typically made of reinforced concrete, masonry, or steel.
- Damping systems: Damping systems help absorb the energy of an earthquake and reduce the amount of shaking felt in a building. These systems can be installed in the building's foundation, floors, or other key structures.
What are the benefits of using earthquake-resistant structures?
There are several benefits of using earthquake-resistant structures:
- Reduced risk of loss of life: Earthquake-resistant structures can minimize the risk of injury or death during an earthquake by ensuring that buildings remain standing and occupants will not be trapped or crushed.
- Less property damage: Earthquake-resistant structures can reduce the extent of property damage caused by earthquakes. This means lower repair and reconstruction costs in the aftermath of an earthquake.
- Increased safety and security: With earthquake-resistant structures, you can feel more secure in facing the unexpected and gain some peace of mind, thus improving the safety and security of occupants.
- Long-term cost savings: While the initial cost of building an earthquake-resistant structure may seem higher, it can save you money in the long run. Since these buildings are more durable, you'll have fewer repairs and maintenance costs down the road.
Earthquake-resistant structures: The bottom line
Earthquake-resistant structures are a vital defense against the unpredictability of earthquakes. With these structures, buildings can withstand the shaking and cracking caused by seismic waves, minimizing injury, death, and property damage. While the upfront costs of building an earthquake-resistant structure can be high, the benefits from reduced repair costs, lower maintenance, and longer lifespan, as well as better safety and security, make it a wise investment in the long run.
FAQs
What is a suspended structure in an earthquake-resistant building?
A suspended structure is a building that hangs from cables or rods. These cables or rods are anchored to a massive concrete foundation or bedrock, and the building is suspended in mid-air. In the event of an earthquake, the suspended structure can move safely and freely while being held secure by the cables or rods, reducing the amount of damage to the building itself.
What is the role of a tuned mass damper in an earthquake-resistant structure?
A tuned mass damper is a device fitted on top of a tall building to keep it steady during an earthquake. It works by counteracting the movements caused by seismic waves and reducing the amount of shaking felt by the occupants. A tuned mass damper is especially important in high-rise buildings, where wind-induced vibrations can also be an issue.
How does base isolation work in an earthquake-resistant structure?
Base isolation involves building the structure on bearings or pads that allow the building to move with the earthquake. This movement-absorbing function distributes the energy of the earthquake, reducing the impact on the building and its occupants. The base isolation method is particularly useful for larger buildings, such as hospitals, high-rise buildings, and stadiums, where thousands of people could gather at any given time.
What materials are commonly used in earthquake-resistant structures?
The most common materials used in earthquake-resistant structures are reinforced concrete, steel, and masonry. These materials are used because of their ability to absorb energy and transfer loads. For example, reinforced concrete and steel can withstand a lot of force, making them ideal materials for seismic-resistant buildings.
What factors affect the design of earthquake-resistant structures?
Several factors affect the design of an earthquake-resistant structure, including the building's size, shape, and location. The building's design takes into account the earthquake's magnitude, how close it is to an active fault line, and what types of seismic waves the area is most susceptible to. Additionally, weather and rainfall conditions, along with the risk of landslides or liquefaction of the soil, can also affect building design.
What is the role of resilience in earthquake-resistant structures?
Resilience is the ability to resist and recover quickly from natural or man-made disasters. In the context of earthquake-resistant structures, resilience means ensuring that buildings and infrastructure remain functional even after an earthquake hits. This includes designing buildings with redundant systems, minimizing the disruptions of critical infrastructure, and emphasizing early warning systems and emergency preparedness.
Overall, earthquake-resistant structures are essential for ensuring safety and security during an earthquake. By using the latest construction techniques and materials, these buildings can withstand the forces of an earthquake and minimize damage to the structure. We hope that this post has demonstrated the value of earthquake-resistant structures and why they are such an important investment. Stay safe!



Post a Comment for "How Does Architecture Incorporate Principles Of Earthquake-resistant Design In Structures?"