How Does Architecture Integrate Principles Of Circular Economy In Construction?

In today's world, sustainability has become the cornerstone of every industry, from fashion to transportation and even food. The built environment is no exception. To address the challenges posed by climate change, resource depletion, and rapid urbanization, the industry needs to embrace new models that promote a circular economy.
But what is a circular economy, and how can it help the built environment become more sustainable? In this post, we'll explore the concept of a circular economy and its application in the built environment. We'll also look at its benefits, challenges, and potential impact on the industry.
What is a circular economy?
A circular economy is an economic model that aims to eliminate waste and promote the efficient use of resources. In a circular economy, materials and products are kept in use for as long as possible, and waste is minimized by designing products that can be easily repaired, reused, recycled, or biodegraded. By keeping materials and products in use for longer, a circular economy can significantly reduce the amount of waste generated and the amount of virgin resources extracted.
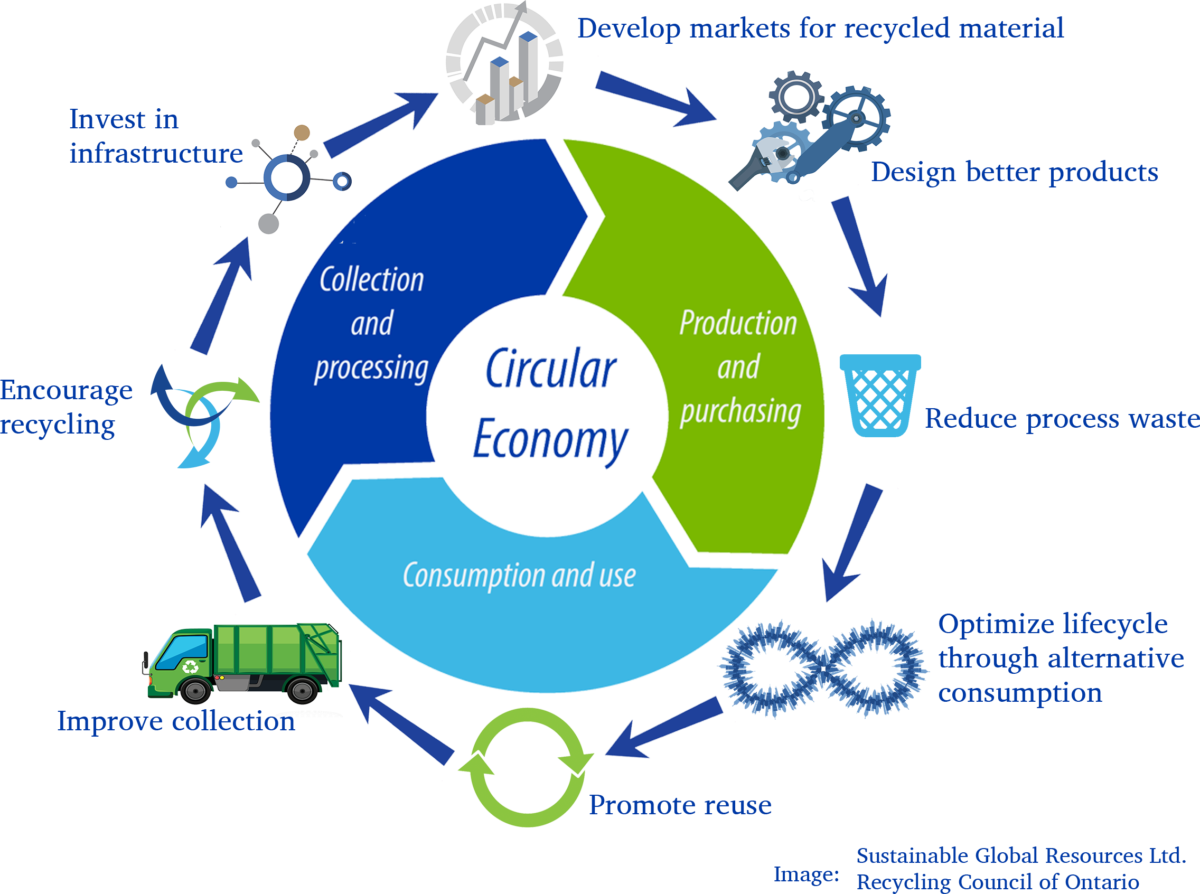
Application of the circular economy in the built environment
The built environment is responsible for a significant amount of waste and resource consumption. From manufacturing and construction to operation and maintenance, every stage of a building's lifecycle has an impact on the environment. To make the built environment more sustainable, we need to adopt a circular approach that optimizes the use of materials, minimizes waste, and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Here are some ways in which a circular economy can be applied to the built environment:
- Design for deconstruction: Buildings should be designed with the end of their lifecycle in mind. This means using materials that can be easily disassembled, reused, or recycled at the end of the building's life.
- Use of recycled materials: The use of recycled materials can significantly reduce the environmental impact of the built environment. Materials such as recycled concrete, plastic, and steel can be used in new construction projects, reducing the need for virgin resources.
- Adoption of prefabricated construction: Prefabricated construction involves the manufacture of building components off-site, which are then assembled on-site. This method reduces waste, minimizes site disruption, and improves the efficiency of construction.
- Efficient use of resources: A circular economy encourages the efficient use of resources, such as energy and water, throughout the building's lifecycle. Buildings should be designed to optimize the use of natural light, ventilation, and heating and cooling systems to reduce energy consumption.
- Biodiversity-friendly design: Buildings can be designed to promote the integration of natural elements, such as green roofs and walls, to create an ecologically balanced environment.
Benefits of a circular economy in the built environment
The adoption of a circular economy in the built environment can have numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced waste: By keeping materials and products in use for longer, a circular economy can significantly reduce the amount of waste generated. It also minimizes the need for landfill sites and incineration, which can have negative environmental and health impacts.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: A circular economy can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reducing resource consumption and energy use. By using renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, a circular economy can help to decarbonize the built environment.
- Improved resource efficiency: The efficient use of resources can result in significant cost savings for building owners and occupants. It can also reduce the reliance on virgin resources, which are often more expensive and environmentally damaging than recycled materials.
- Improved occupant health and wellbeing: A circular economy can promote the integration of natural elements into buildings, such as daylight and greenery, which can have positive impacts on occupant health and wellbeing.
Challenges of implementing a circular economy in the built environment
While a circular economy has many benefits, it also poses significant challenges for the built environment. Here are some of the challenges:
- Lack of awareness: A circular economy is a relatively new concept, and many stakeholders in the built environment may not be aware of its potential benefits.
- Inadequate infrastructure: The integration of circular principles into the built environment requires significant changes to the current infrastructure and built environment practices. Without adequate infrastructure support, it will be challenging to implement a circular economy.
- Higher initial costs: The adoption of a circular economy may require higher initial capital costs due to the use of novel materials and design approaches, which can deter some investors.
- Limited availability of recycled materials: Despite the increasing demand for recycled materials, they remain relatively scarce and expensive, limiting their availability in the built environment.
FAQs
What is the built environment?
The built environment refers to the human-made environment that includes buildings, infrastructure, and cities.
What is resource depletion?
Resource depletion refers to the depletion of natural resources, such as land, water, and energy, caused by overuse and unsustainable consumption practices.
What is the difference between recycling and upcycling?
Recycling involves the transformation of waste materials into new materials, whereas upcycling involves the transformation of waste materials into products of higher value or quality.
Conclusion
A circular economy is a promising approach to sustainability in the built environment. It has the potential to reduce waste, improve resource efficiency, and mitigate climate change impacts. However, the adoption of a circular economy in the built environment requires significant changes to the current infrastructure and practices. With adequate awareness, infrastructure, and investment support, we can create a built environment that is sustainable, resilient, and equitable for all.



Post a Comment for "How Does Architecture Integrate Principles Of Circular Economy In Construction?"