How Does Architecture Integrate Principles Of Water-sensitive Design?
In today's world, urbanization is at an all-time high, and with it, comes an ever-increasing number of challenges. One such challenge is the efficient and sustainable management of water in our cities. This is where "Water Sensitive Urban Design" comes into the picture. By taking inspiration from nature and implementing sustainable techniques, this design approach ensures that cities can manage their water resources in a way that is efficient and environmentally-friendly.
In this post, we will be discussing Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD) in detail and exploring its benefits and applications.
What is Water Sensitive Urban Design?
Water Sensitive Urban Design, or WSUD, is a design philosophy that aims to create sustainable water management systems in urban and suburban environments. It advocates for a holistic, integrated approach to urban water management that takes into account the urban water cycle from source to sea.
How Does Water Sensitive Urban Design Work?
The basic idea behind WSUD is to mimic nature's way of managing water. This is achieved by using a combination of natural and engineered systems to manage water at its source. The approach aims to reduce the volume of water entering the drainage system by using techniques like rainwater harvesting, infiltration, and evapotranspiration. The collected water is then stored, treated, and reused for various purposes.
Benefits of Water Sensitive Urban Design
Water Sensitive Urban Design has numerous benefits for both the environment and the communities it serves. Here are some of the most significant benefits:
- Improved Water Quality: By intercepting polluted runoff and treating it before it enters waterways, WSUD helps to improve water quality.
- Reduced Flooding: By using infiltration techniques, WSUD reduces the risk of flooding caused by heavy rainfall.
- Reduced Water Demand: By using harvested rainfall for non-potable purposes, WSUD helps to reduce the demand for municipal water supplies.
- Improved Biodiversity: WSUD provides habitat for various fauna and flora species by creating green spaces and wetlands.
- Energy Savings: By reducing the demand for water and treating water on-site, WSUD helps to reduce energy consumption.
Applications of Water Sensitive Urban Design
WSUD can be applied across various urban environments, including residential, commercial, industrial, and institutional properties. Some of the most common applications include:
- Green Roofs: Installing vegetation and soil on building roofs to capture and absorb rainfall.
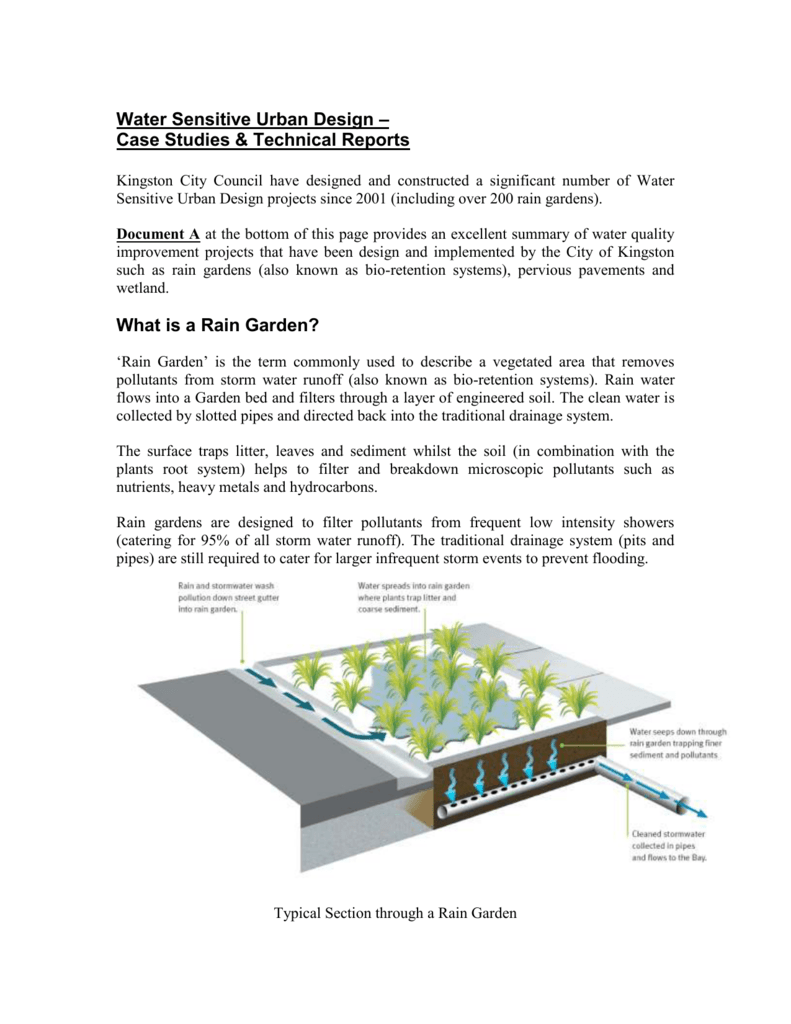
- Rain Gardens: Designing and landscaping shallow depressions that capture and absorb rainwater from roofs and other impervious surfaces.
- Bio-Retention Basins: Creating shallow earthen depressions filled with vegetation to capture and filter stormwater runoff.
- Permeable Pavements: Using porous materials for roads and parking lots to allow water to infiltrate rather than run off.
- Stormwater Harvesting Systems: Collecting, storing, treating, and reusing rainwater for non-potable purposes.
FAQs
1. How does WSUD help to reduce flooding?
WSUD intercepts and infiltrates rainfall at its source, reducing the amount of water that enters the municipal drainage system. By reducing the volume of water that enters the system during a large rainfall event, WSUD helps to reduce the risk of flooding.
2. Can WSUD be applied in all urban environments?
Yes, WSUD can be applied across various urban environments, including residential, commercial, industrial, and institutional properties. However, the specific application of WSUD needs to be adapted to suit the local environment, climate, and water resources.
3. Is WSUD cost-effective?
Implementing WSUD systems may involve higher upfront costs than traditional water management systems. However, the long-term benefits for both the environment and the community well-being usually outweigh the costs in the long run. Moreover, WSUD techniques can also help to reduce water and energy bills by reducing the demand for municipal supplies.
4. Are there any drawbacks to WSUD?
WSUD may be limited by the availability of water resources and land in urban environments. Moreover, WSUD systems require regular maintenance to ensure their proper functioning, which can be a challenge in densely populated urban areas.
5. What is the future of WSUD?
With the growing threat of urbanization and climate change, WSUD is becoming an increasingly important design approach for managing water in the urban environment. It is expected that in the coming years, WSUD will become a standard practice for urban water management worldwide.
In conclusion, Water Sensitive Urban Design is a holistic, sustainable approach to urban water management that aims to mimic nature's way of managing water. It has numerous environmental and community benefits and can be applied across various urban environments. With its future looking bright, WSUD is sure to play a key role in ensuring the sustainable future of our cities.


Post a Comment for "How Does Architecture Integrate Principles Of Water-sensitive Design?"